Introduction
The kidney stone size chart categorizes stones as small (1-2 mm), medium (3-6 mm), large (7-9 mm), and very large (10 mm+). Treatment varies by size, ranging from home remedies for smaller stones to surgical options for larger ones.
A. Kidney stones are hardened deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys.
B. The size of a kidney stone is an important factor in determining the appropriate treatment and prognosis.
C. This article will provide an overview of kidney stones, their sizes, and the implications for treatment and prevention.
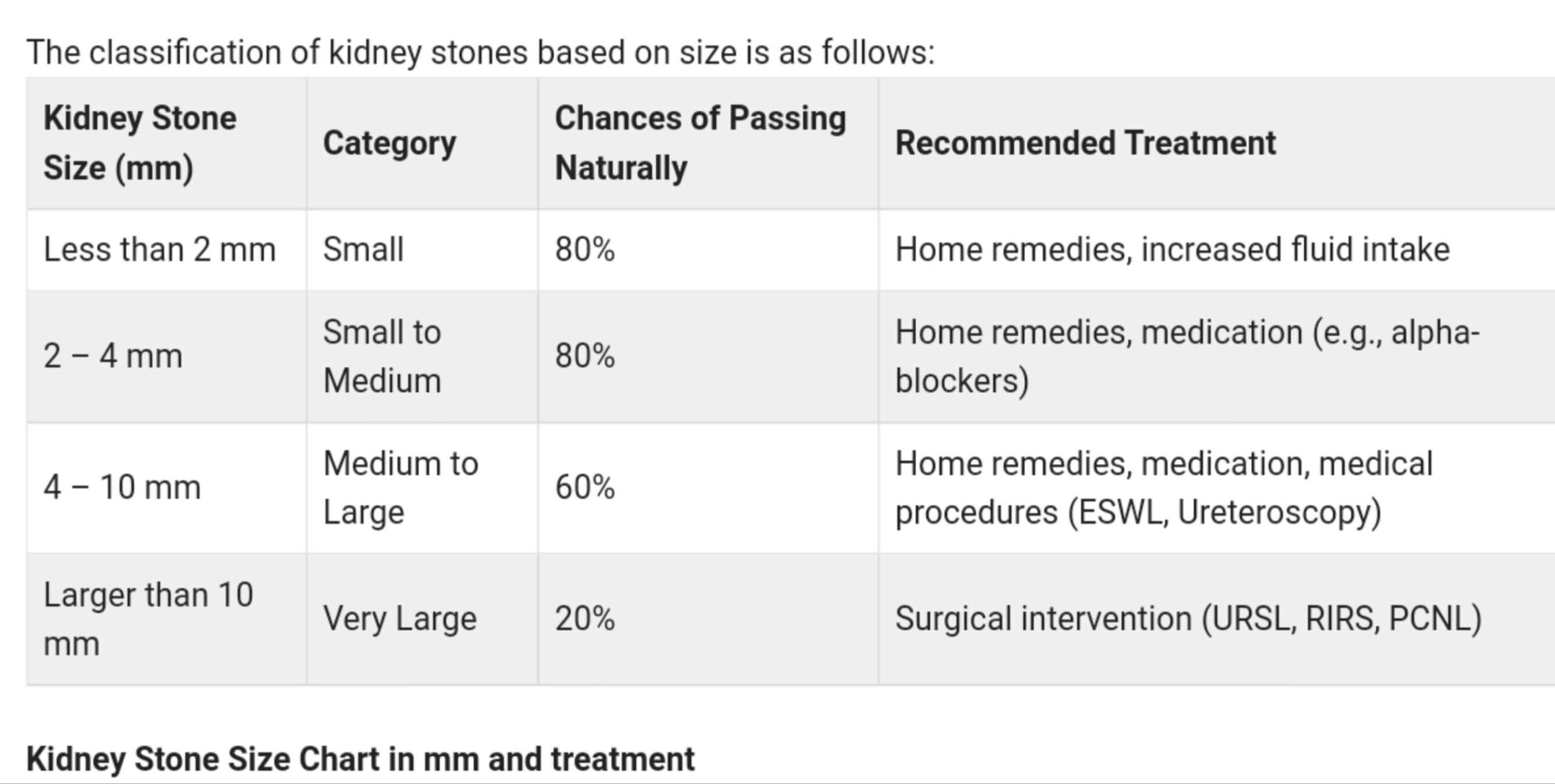
The classification of kidney stones based on size is as follows:
| Kidney Stone Size (mm) | Category | Chances of Passing Naturally | Recommended Treatment |
| Less than 2 mm | Small | 80% | Home remedies, increased fluid intake |
| 2 – 4 mm | Small to Medium | 80% | Home remedies, medication (e.g., alpha-blockers) |
| 4 – 10 mm | Medium to Large | 60% | Home remedies, medication, medical procedures (ESWL, Ureteroscopy) |
| Larger than 10 mm | Very Large | 20% | Surgical intervention (URSL, RIRS, PCNL) |
Kidney Stone Size Categories
Small (1-2 mm): 80% chance of passing naturally, treated with home remedies and increased fluid intake
Medium (3-6 mm): 80% chance of passing naturally, treated with home remedies and medication (e.g. alpha-blockers)
Large (7-9 mm): 60% chance of passing naturally, treated with home remedies, medication, and medical procedures like ESWL or ureteroscopy
Very Large (10 mm+): 20% chance of passing naturally, requires surgical intervention like URSL, RIRS, or PCNL
Kidney Stone Size Measurement methods
– Stones are typically measured in millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm).
– Imaging tests provide an accurate measurement of the stone size.
Kidney stones vary in size and treatment options, which are crucial for effective management. Here’s a detailed overview of kidney stone sizes in millimeters (mm) and the corresponding treatment approaches.
Treatment Options for kidney stone
Conservative Management
Kidney stones less than 4 mm size, conservative measures such as increased hydration and pain management are usually effective.
Medical Procedures
Kidney stones size between 4 mm and 10 mm, treatments may include:
1. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): A non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves to break stones into smaller pieces.
2. Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy (URSL): Involves the use of a ureteroscope to locate and remove stones, often using laser technology for fragmentation.
Surgical Options
Kidney stones size larger than 10 mm, surgical options are necessary:
1. Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS): A minimally invasive procedure to remove stones directly from the kidney.
2. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): A more invasive procedure involving a small incision to access and remove large stones.
Diagnosis
– Diagnosis is based on symptoms, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scan.
– Blood and urine tests can help identify the type of stone and underlying causes.
Conclusion
The kidney stone size chart categorizes stones as small (1-2 mm), medium (3-6 mm), large (7-9 mm), and very large (10 mm+). Treatment varies by size, ranging from home remedies for smaller stones to surgical options for larger ones.