
By Adam | Published November 13, 2025
Quick answer: Persistent thirst, frequent urination, unexplained fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds indicate elevated blood glucose. Confirm diagnosis with fasting blood glucose, A1C, or oral glucose toleranc

By Adam | Published November 13, 2025
Quick answer: Persistent thirst, frequent urination, unexplained fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds indicate elevated blood glucose. Confirm diagnosis with fasting blood glucose, A1C, or oral glucose tolerance tests.
Quick summary
- Symptoms: excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, slow wound healing.
- Tests: fasting glucose, A1C, and oral glucose tolerance test.
- Risk groups: overweight adults, family history, gestational diabetes history.
Introduction: The silent condition that changes metabolism
Diabetes develops gradually and damages blood vessels and nerves before symptoms become obvious. Hundreds of millions live with diabetes, often undiagnosed. This guide explains what to watch for, which tests confirm the diagnosis, and the steps that protect your organs and lifespan.
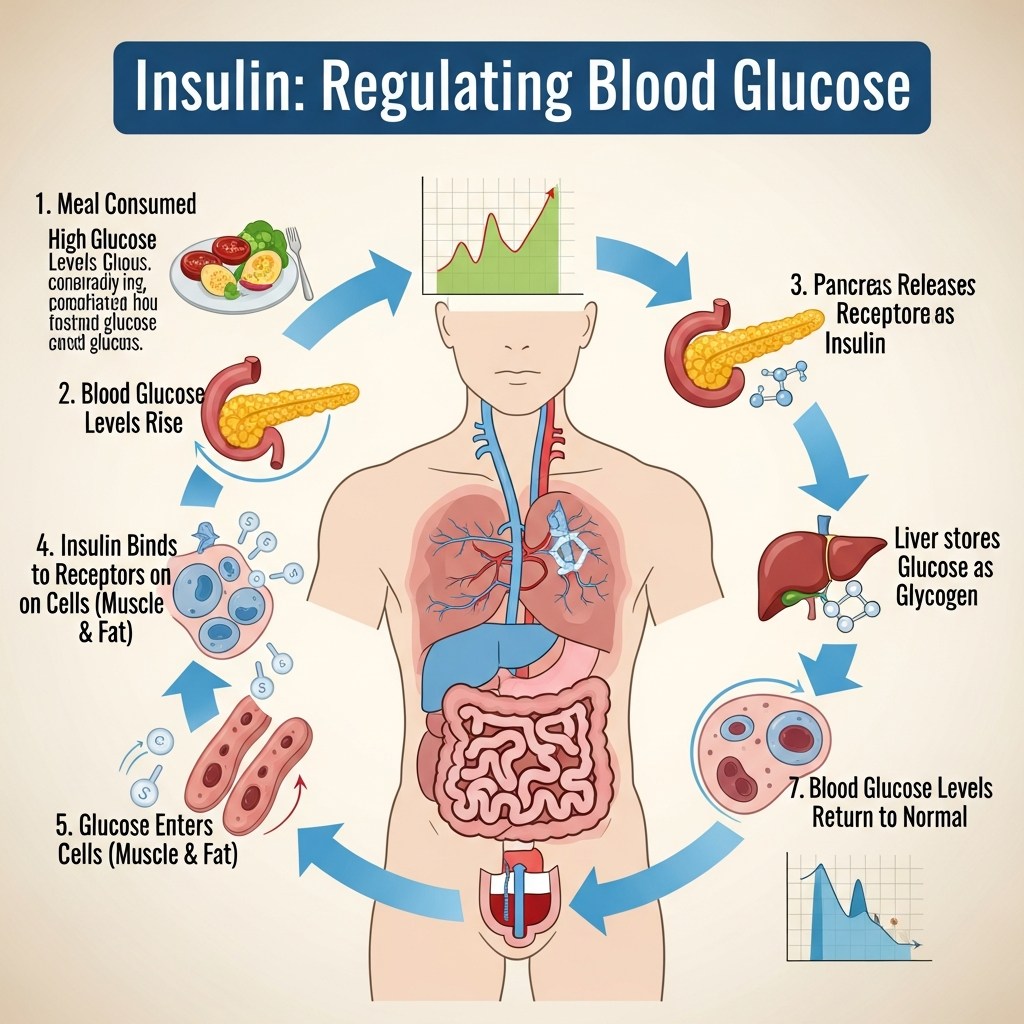
Understanding diabetes: the basic pathology
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder where insulin fails to regulate blood glucose. The body either produces too little insulin or cannot use it efficiently, leading to persistent hyperglycemia and organ damage.
Types of diabetes
- Type 1: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells; requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2: Insulin resistance combined with relative insulin deficiency; associated with obesity and inactivity.
Primary warning signs you must not ignore

Excessive thirst and frequent urination
High blood glucose draws fluid from tissues, triggering dehydration and constant thirst. Nighttime urination is often the first physical sign of dysregulated glucose.
Unexplained fatigue
When glucose cannot enter cells, energy production drops. Persistent exhaustion even after rest indicates glucose imbalance.
Slow wound healing
Elevated glucose damages blood vessels, slowing oxygen delivery to tissues. Even small cuts can take weeks to heal—a clear red flag that glucose levels are uncontrolled.
Blurred vision and numbness
Fluctuating glucose disturbs eye focus and damages peripheral nerves, leading to vision changes and tingling in the extremities.
How clinicians confirm the diagnosis

| Test | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting Blood Glucose | <100 mg/dL | 100–125 | ≥126 on 2 occasions |
| A1C | <5.7% | 5.7–6.4% | ≥6.5% |
| OGTT (2-hour) | <140 mg/dL | 140–199 | ≥200 |
Who should get tested and how often
- Adults aged 40+
- People with obesity or family history
- History of gestational diabetes
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
Prediabetes is reversible

- Lose 5–10% of body weight.
- Exercise 30 minutes daily.
- Limit refined sugars and processed carbs.
- Prioritize 7–8 hours of sleep and stress control.
Real patient example

Maria, 42, ignored early symptoms until testing confirmed diabetes. Within six months of structured nutrition and medication, she regained metabolic control and prevented further complications.
Complications of untreated diabetes
Without intervention, hyperglycemia leads to cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy. Early control prevents irreversible organ damage.

People Also Ask
Yes. Many individuals live with undiagnosed diabetes for years. Regular screening identifies silent cases early.
Chronic stress increases cortisol, leading to elevated blood sugar and insulin resistance.
Related Topic
About the author: Dr Adam is a medical researcher and health writer specializing in metabolic diseases. Their work focuses on evidence-based prevention and clinical communication.

