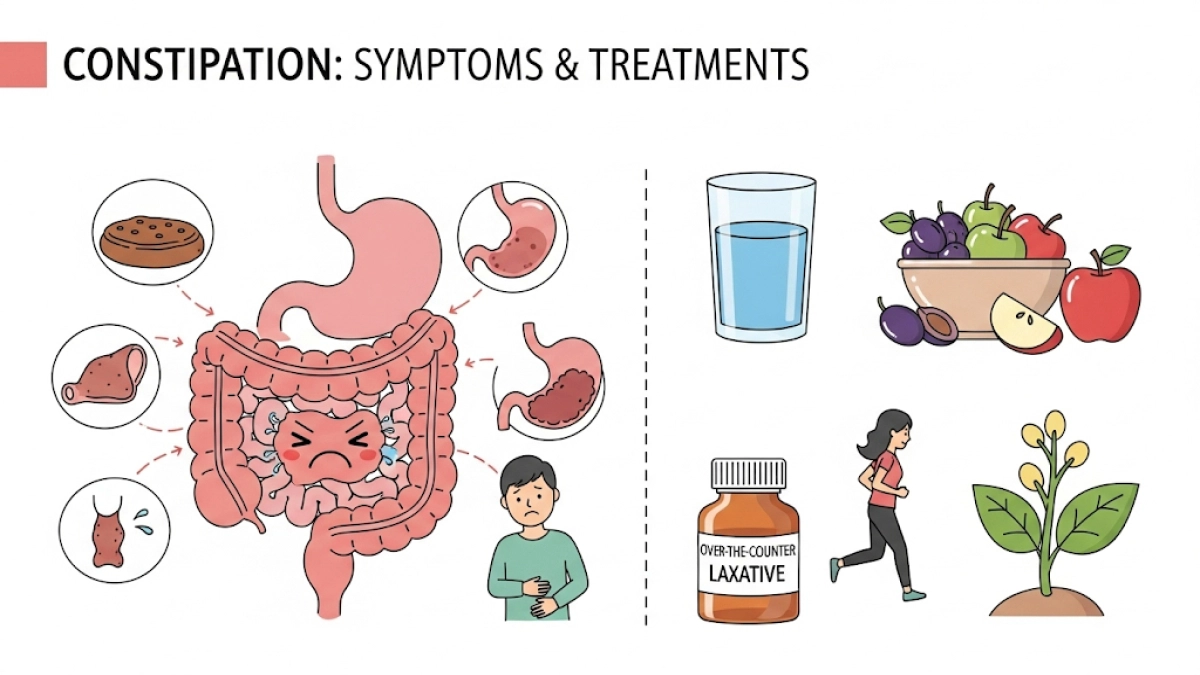
Constipation is a common yet often misunderstood digestive issue that affects millions worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people suffer in silence, unsure of when to seek help or how to effectively manage their symptoms.
As we approach 2025, evolving search algorithms prioritize content that demonstrates deep expertise, experience, and trustworthiness—qualities essential for health-related topics. This article aims to deliver a comprehensive, nuanced exploration of constipation symptoms and treatments, blending expert analysis, practical wisdom, and the latest research to empower readers with actionable knowledge.
Understanding Constipation: More Than Just Infrequent Bowel Movements
At its core, constipation is characterized by difficulty passing stool or infrequent bowel movements, typically fewer than three per week. However, the experience of constipation is highly individual and can include a spectrum of symptoms beyond frequency alone.
Common Symptoms of Constipation
- Hard, dry stools that are painful or difficult to pass
- Straining during bowel movements
- A sensation of incomplete evacuation
- Abdominal discomfort or bloating
- Feeling of blockage in the rectum
- Occasionally, rectal bleeding due to straining or hemorrhoids
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial. Many people dismiss constipation as a minor inconvenience, but chronic constipation can lead to complications such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or even fecal impaction.
Expert Insight: Gastroenterologists emphasize that the quality of bowel movements—such as stool consistency and ease of passage—is often more telling than frequency alone. This nuanced understanding helps tailor treatment strategies effectively.
Root Causes: Why Does Constipation Occur?
Constipation is rarely a standalone condition; it often signals underlying lifestyle factors, medical conditions, or medication side effects.
Primary Causes Include:
- Dietary factors: Low fiber intake, inadequate hydration
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity slows intestinal motility
- Medications: Opioids, antacids containing aluminum or calcium, certain antidepressants
- Medical conditions: Hypothyroidism, diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), neurological disorders
- Psychological factors: Stress and anxiety can disrupt gut function
Understanding the root cause is essential for effective treatment. For example, constipation caused by medication may require a different approach than constipation linked to dietary habits.
Diagnosing Constipation: When to See a Doctor
While occasional constipation is common, persistent or severe symptoms warrant professional evaluation. Warning signs include:
- Sudden change in bowel habits lasting more than two weeks
- Blood in stool or black, tarry stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Severe abdominal pain or bloating
- Constipation alternating with diarrhea
A healthcare provider may perform a physical exam, review medical history, and order tests such as blood work, colonoscopy, or imaging studies to rule out serious conditions.
Treatment Strategies: From Lifestyle to Medical Interventions
Addressing constipation effectively requires a multi-pronged approach tailored to individual needs.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Increase dietary fiber: Aim for 25-30 grams daily from fruits, vegetables, whole grains
- Hydration: Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily to soften stool
- Regular exercise: Activities like walking stimulate bowel motility
- Establish a routine: Respond promptly to bowel urges and consider scheduled bathroom times
2. Over-the-Counter Remedies
- Bulk-forming laxatives: Psyllium, methylcellulose increase stool bulk and promote movement
- Osmotic laxatives: Polyethylene glycol draws water into the colon to soften stool
- Stool softeners: Docusate sodium helps ease passage without stimulating the bowel
- Stimulant laxatives: Senna or bisacodyl induce bowel contractions but should be used sparingly
3. Prescription Treatments
For chronic or refractory constipation, doctors may prescribe medications such as:
- Lubiprostone: Increases intestinal fluid secretion
- Linaclotide: Enhances bowel transit and reduces pain in IBS-related constipation
- Prucalopride: A serotonin receptor agonist that stimulates colonic motility
4. Advanced Therapies
In rare cases, biofeedback therapy or surgery may be necessary, especially when constipation results from pelvic floor dysfunction or anatomical abnormalities.
Integrating Holistic and Emerging Approaches
Beyond conventional treatments, emerging research highlights the gut microbiome’s role in bowel health. Probiotics and prebiotics may offer adjunctive benefits by restoring microbial balance, though evidence remains evolving.
Mind-body techniques such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture have also shown promise in alleviating constipation symptoms by reducing stress and improving autonomic nervous system regulation.
Practical Wisdom: Tips for Long-Term Relief
- Track your symptoms: Keeping a bowel diary can help identify triggers and monitor treatment effectiveness.
- Avoid over-reliance on laxatives: Chronic use can worsen bowel function. Use under medical supervision.
- Prioritize fiber variety: Soluble and insoluble fibers serve different roles; a balanced intake is key.
- Stay patient: Dietary and lifestyle changes may take weeks to show results. Consistency is vital.
Latent User Queries Addressed
- Can dehydration cause constipation? Yes, insufficient fluid intake hardens stool, making it difficult to pass.
- Is constipation dangerous? Usually not, but chronic constipation can lead to complications if untreated.
- How does stress affect constipation? Stress alters gut motility and sensitivity, often worsening symptoms.
- Are natural remedies effective? Some, like fiber and probiotics, have evidence backing their use, but results vary.
Sections Ripe for Augmentation
- Proprietary Data: Incorporate patient survey results on constipation symptom patterns and treatment outcomes.
- Personal Anecdotes: Share real-life stories from individuals who overcame chronic constipation through lifestyle changes.
- Expert Citations: Include quotes or interviews with gastroenterologists or dietitians to enhance credibility.
Conclusion: Empowering You to Take Control of Constipation
Constipation is more than a mere inconvenience; it is a signal from your body that something needs attention. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and a spectrum of treatment options—from lifestyle tweaks to advanced therapies—you can reclaim digestive health and improve quality of life. Remember, persistent symptoms deserve professional evaluation, and a personalized approach is always best.